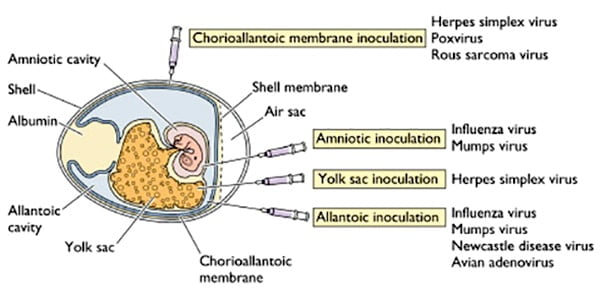
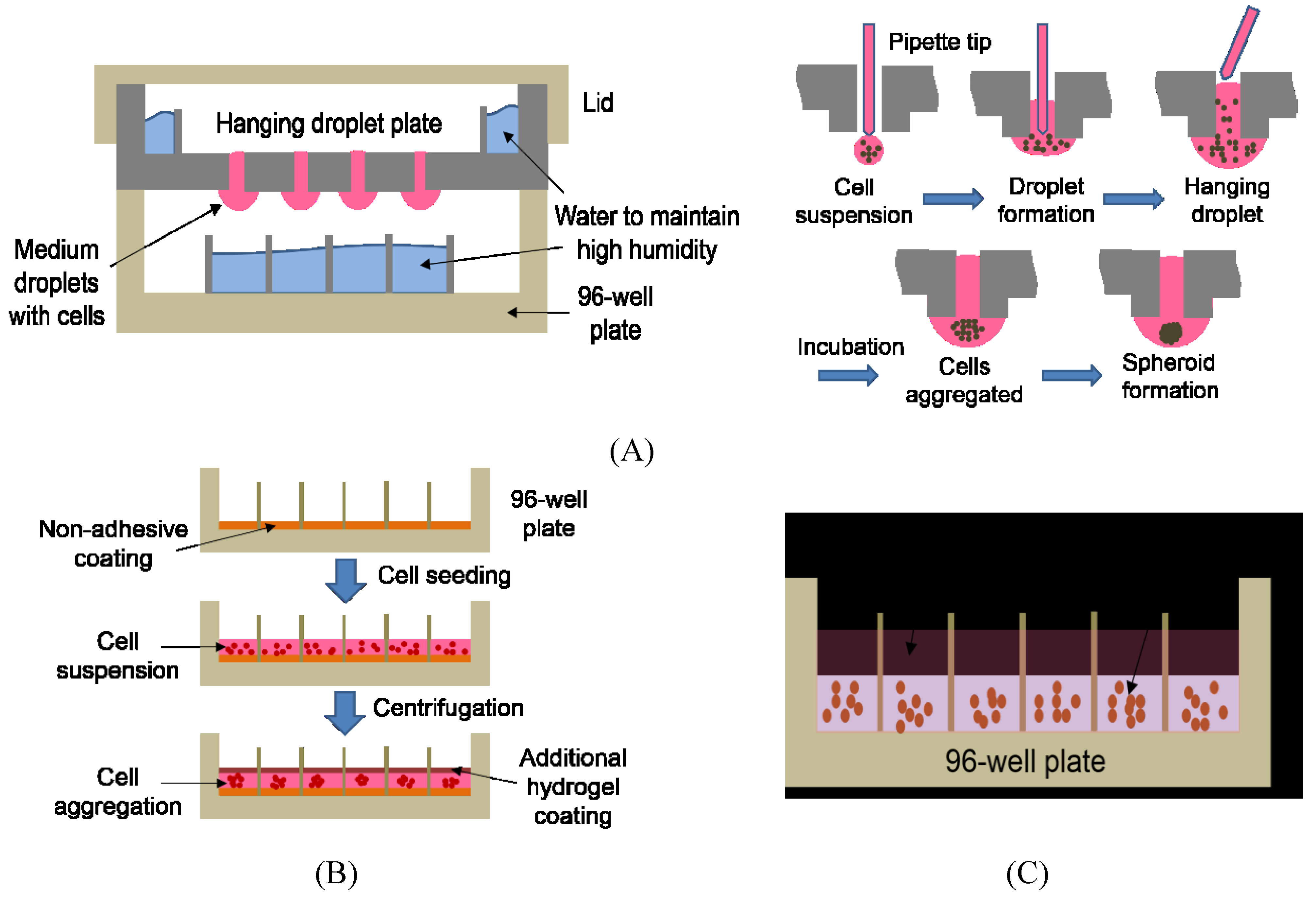
Human Cell Culture Techniques

The growth can be characterized by cell division mitosis or by other processes such as differentiation during which the cells can change into.
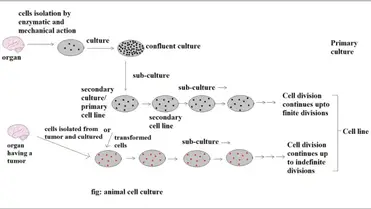
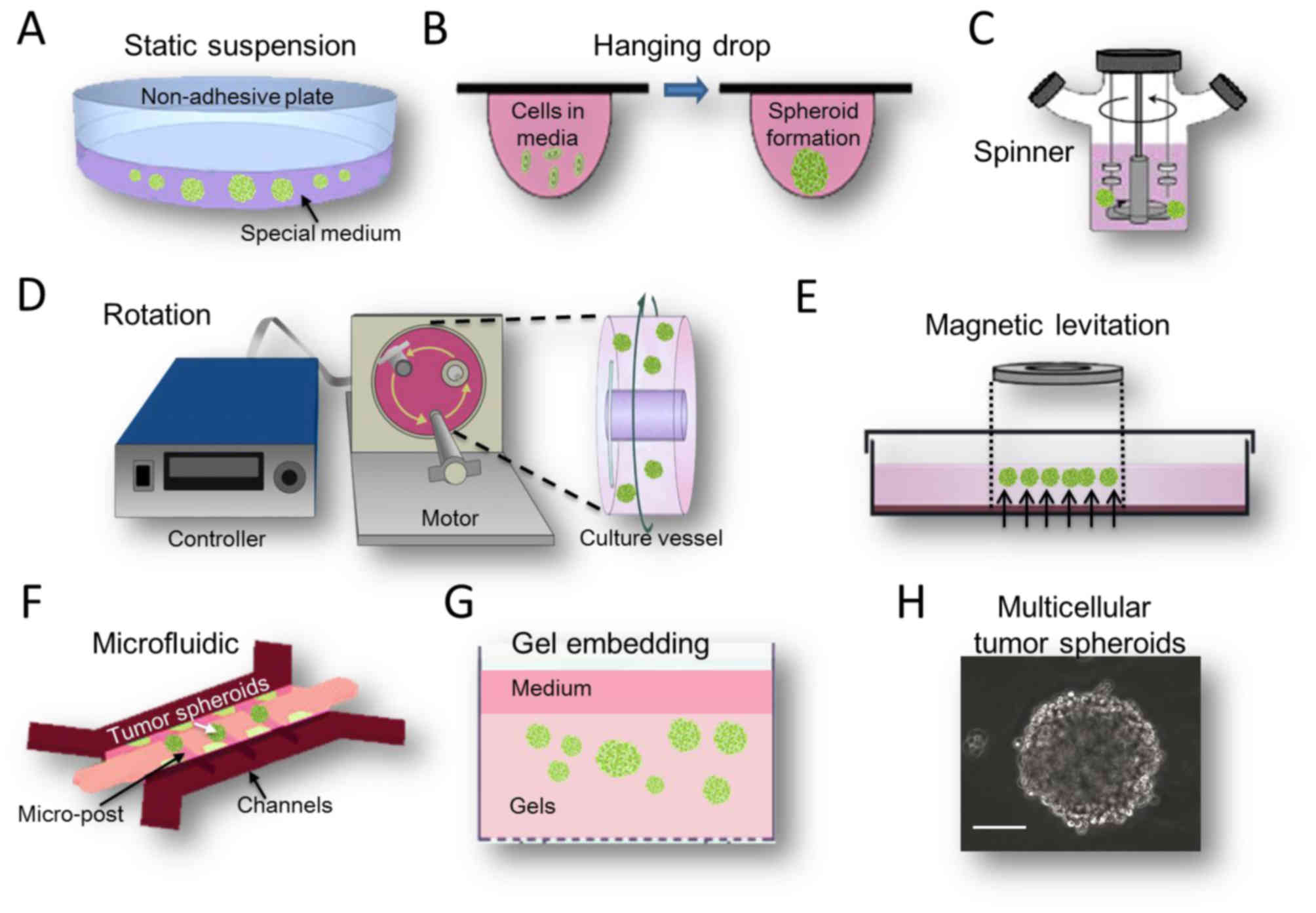
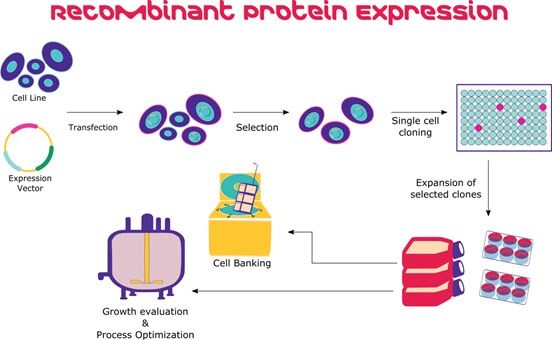
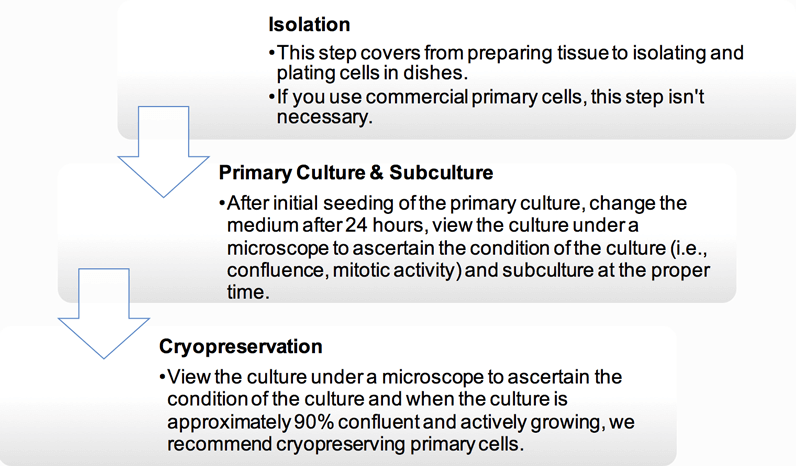
Human cell culture techniques. Cell culture cell culture is one of the major tools used in cellular and molecular biology providing excellent model systems for studying the normal physiology and biochemistry of cells e g metabolic studies aging the effects of drugs and toxic compounds on the cells and mutagenesis and carcinogenesis. There are very common areas of use in cell cultures. Cell culture basics techniques and media essentially cell culture involves the distribution of cells in an artificial environment in vitro which is composed of the necessary nutrients ideal temperature gases ph and humidity to allow the cells to grow and proliferate. Primary cell culture applications.
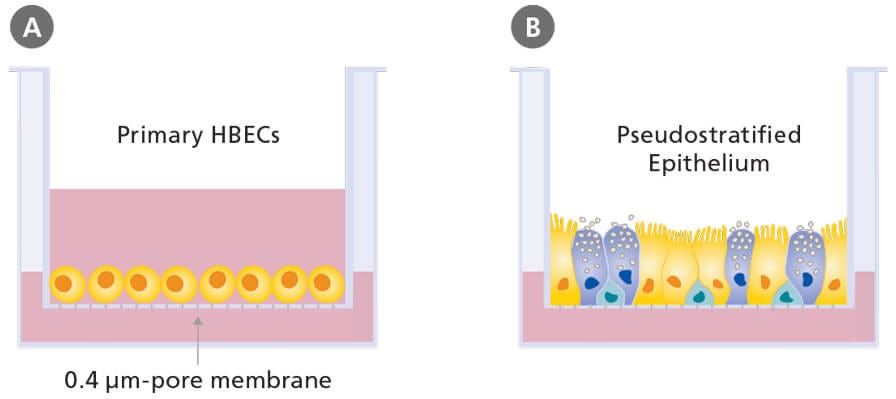
Primary cell culture is increasingly being used as a major tool in cellular and molecular biology providing excellent model systems for studying the normal physiology and biochemistry of cells e g metabolic studies aging signaling studies the effects of drugs and toxic compounds on the cells and mutagenesis and carcinogenesis. The areas in which the cell culture is used can be counted as monoclonal antibody viral and insect vaccine enzyme hormone interleukin and growth factor productions. Cell culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions generally outside their natural environment. The following is an example for endothelial and epithelial cells.
Cell culture is basically reproduction and survival of cells in an artificial environment. For human cells coat flasks with 1 gelatin. Prepare 10ml of coating solution composed of 1 gelatin or 1 fibronectin by diluting with distilled water followed by filtration. Lynn in encyclopedia of insects second edition 2009.
In vivo when the study involves living biological entities within the organism. After the cells of interest have been isolated from living tissue they can subsequently be maintained under carefully controlled conditions these conditions vary for each cell type but generally consist of a suitable vessel with a substrate or medium that supplies.